Research Area E - Publications 2008
24-Dec-2008
J. Pep. Sci., 2009, 15(2), 58-66, doi:10.1002/psc.1107 published on 24.12.2008
Journal of Peptide Science, online article
Since the discovery of the proteasome and its structure elucidation intensive research programs in academic institutions and pharmaceutical industries led to identification of a wide spectrum of synthetic and natural small proteasomal inhibitors. Activity studies with these small molecules helped to deeply understand the complex biochemical organization and ...
15-Dec-2008
Organometallics, online article
Electrospray ionization (ESI) of mixtures of organolithium compounds and zinc chloride in tetrahydrofuran produced manifold mono- and polynuclear organozincate anions. Formation of the latter is strongly favored by the incorporation of chloride ligands, which apparently adopt bridging binding modes. Analysis of LinBu/ZnCl2 solutions at different concentrations ...
12-Dec-2008

DNA photolyases and cryptochromes (cry) form a family of flavoproteins that use light energy in the blue/UV-A region for the repair of UV-induced DNA lesions or for signaling, respectively. Very recently, it was shown that members of the DASH cryptochrome subclade repair specifically cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) in UV-damaged single-stranded DNA. Here, we ...
08-Dec-2008

The “seventeen kilodalton protein” (Skp) is a predominant periplasmic chaperone of Escherichia coli, which is involved in the biogenesis of abundant outer membrane proteins (OMPs) such as OmpA, PhoE, and LamB. In this study the substrate profile of Skp was investigated in a proteomics approach. Skp was overexpressed in a deficient E. coli strain as a fusion ...
25-Nov-2008
Deutschland Land der Ideen

YEAH! CIPSM ist „Ausgewählter Ort im Land der Ideen“. Damit ist CIPSM Teil der Veranstaltungsreihe „365 Orte im Land der Ideen“, die gemeinsam von der Standortinitiative „Deutschland – Land der Ideen“ und der Deutschen Bank durchgeführt wird. Als „Ausgewählter Ort“ wird CIPSM unter der Schirmherrschaft von Bundespräsident Horst Köhler im Jahr 2009 Deutschland als ...
21-Nov-2008
Small noncoding RNAs function in concert with Argonaute (Ago) proteins to regulate gene expression at the level of transcription, mRNA stability, or translation. Ago proteins bind small RNAs and form the core of silencing complexes. Here,wereport the analysis of small RNAs associated with human Ago1 and Ago2 revealed by immunoprecipitation and deep sequencing. ...
14-Nov-2008
An investigation of the precise interactions between damaged DNA and DNA repair enzymes is required in order to understand the lesion recognition step, which is one of the most fundamental processes in DNA repair. Most recently, photoaffinity labeling approaches have enabled the analysis of even transient protein- DNA interactions. Here we report the synthesis ...
06-Nov-2008
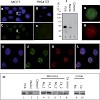
Large-scale analysis directly at the protein level holds the promise of uncovering features not apparent or present at the gene level [1,2,3]. Although mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics can now identify and quantify thousands of cellular proteins in large-scale proteomics experiments, much of the peptide information contained in these experiments remains ...
02-Nov-2008
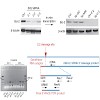
Genetic and epigenetic plasticity allows tumors to evade single-targeted treatments. Here we direct Bcl2-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) with 5¢-triphosphate ends (3p-siRNA) against melanoma. Recognition of 5¢-triphosphate by the cytosolic antiviral helicase retinoic acid–induced protein I (Rig-I, encoded by Ddx58) activated innate immune cells such as ...
02-Nov-2008
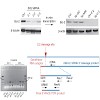
Genetic and epigenetic plasticity allows tumors to evade single-targeted treatments. Here we direct Bcl2-specific short interfering RNA (siRNA) with 5¢-triphosphate ends (3p-siRNA) against melanoma. Recognition of 5¢-triphosphate by the cytosolic antiviral helicase retinoic acid–induced protein I (Rig-I, encoded by Ddx58) activated innate immune cells such as ...
30-Oct-2008
Journal of Molecular Biology, 2009, 385, 3, 912 - 923 published on 30.10.2008
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

Specific interactions of transmembrane helices play a pivotal role in the folding and oligomerization of integral membrane proteins. The helix–helix interfaces frequently depend on specific amino acid patterns. In this study, a heptad repeat pattern was randomized with all naturally occurring amino acids to uncover novel sequence motifs promoting transmembrane ...
27-Oct-2008
Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed., online article
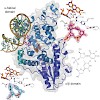
UV irradiation of cells gives rise to the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) and so-called (6-4) DNA lesions (Scheme 1). Both lesions are major photoproducts formed in dipyrimidine sequences of double-stranded DNA. Repair of these lesions is essential because of their high mutagenic potential. Particularly important in many organisms are the ...
21-Oct-2008

We have recently identified the archaic cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) as a non-canonical ligand of the CXC chemokine receptors CXCR2 and CXCR4 in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Because its affinity for CXCR2 was particularly high, we hypothesized that MIF may feature structural motives shared by canonical CXCR2 ligands, ...
21-Oct-2008
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, online article
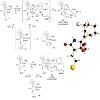
Salinosporamide A (1 (NPI-0052)) is a potent, monochlorinated 20S proteasome inhibitor in clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. To elucidate the role of the chlorine leaving group (LG), we synthesized analogues with a range of LG potentials and determined their IC50 values for inhibition of chymotrypsin-like (CT-L), trypsin-like (T-L), and caspase-like ...
21-Oct-2008
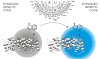
Our long-term goal is the in vivo expression of intrinsically colored proteins without the need for further posttranslational modification or chemical functionalization by externally added reagents. Biocompatible (Aza)Indoles (Inds)/(Aza)Tryptophans (Trp) as optical probes represent almost ideal isosteric substitutes for natural Trp in cellular proteins. To ...
17-Oct-2008
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
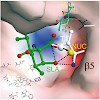
Spiro β-lactone-based proteasome inhibitors were discovered in the context of an asymmetric catalytic total synthesis of the natural product (+)-lactacystin (1). Lactone 4 was found to be a potent inhibitor of the 26S proteasome, while its C-6 epimer (5) displayed weak activity. Crystallographic studies of the two analogues covalently bound to the 20S proteasome ...
14-Oct-2008
BIONRM

The winners of the second ever Innovation Award of the German BioRegions were announced on the 7th October – Thomas Böttcher together with Dr. Stephan Sieber from CIPSM were awarded joint prizes by Director General from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research together with Dr. Heinz Bettmann, BioCologne e.V. representing this year’s sponsors. The ...
11-Oct-2008
JACS, online article
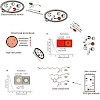
With the evolution of multidrug resistant bacterial pathogens, infectious diseases pose once again a serious threat to public health. Especially the opportunistic pathogen Staphylococcus aureus has gained importance through the dramatically increasing appearance of methicillin-resistant (MRSA) strains in hospitals and the recent emergence of epidemic ...
22-Sep-2008
Angewandte Chemie Int. Ed., online article
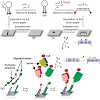
The attachment of labels onto DNA is of utmost importance in many areas of biomedical research and is valuable in the construction of DNA-based functional nanomaterials. The copper(I)-catalyzed Huisgen cycloaddition of azides and alkynes (CuAAC) has recently been added to the repertoire of DNA labeling methods, thus allowing the virtuallyunlimited ...
16-Sep-2008
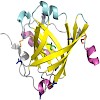
α1-Acid glycoprotein (AGP) is an important drug-binding protein in human plasma and, as an acute-phase protein, it has a strong influence on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of many pharmaceuticals. We report the crystal structure of the recombinant unglycosylated human AGP at 1.8 Å resolution, which was solved using the new method of UVradiation- ...
10-Sep-2008
JACS, online article
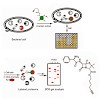
With the development of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains, infectious diseases have become again a life-threatening problem. One of the reasons for this dilemma is the limited number and breadth of current therapeutic targets for which several resistance strategies have evolved over time. To expand the number of addressable enzyme targets and to understand ...
10-Sep-2008

2008 is great! Ein hochrangiger Wissenschaftler kündigt seine Stelle an der Eliteuniversität Berkeley, weil er lieber an einer deutschen Universität arbeiten möchte - und bringt auch gleich sein ganzes Forschungsteam mit. pdf link
05-Sep-2008
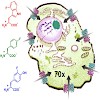
Nonproteinogenic amino acids that either occur naturally or are synthesized chemically are becoming important tools in modern drug discovery. In this context, fluorinated amino acids have great potential in the development of novel pharmaceuticals and drugs. To assess whether different fluorinated aromatic amino acid analogues of phenylalanine, tyrosine, and ...
27-Aug-2008
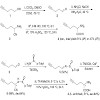
An improved classic Strecker synthesis was elaborated leading to racemic homopropargylglycine (Hpg) in 61% overall yield, while an asymmetric Strecker reaction produced Hpg and the higher homolog 2-aminohept-6-ynoic acid in significantly higher yields and over 80% ee.
22-Aug-2008
BioMed Central, online article
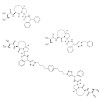
Protein-protein interactions regulate almost all aspects of cellular signaling and aberrant protein-protein interactions have the potential to cause or contribute to human disease. The modulation of these interactions by drug-like molecules would offer previously unavailable opportunities to explore the relevance of pre-selected protein-protein interactions for ...
13-Aug-2008
ScienceDirect, online article
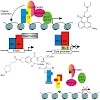
Gene-specific transcription factors are DNA binding proteins that function at the center of the transcriptional machinery to mediate the cellular phenotype in response to extracellular signals. Owing to the lack of enzymatic activities of these intracellular proteins, manipulating the activity of transcription factors by small organic molecules is widely ...
08-Aug-2008
Angewandte Chemie, online article
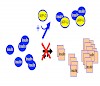
In vivo protein aggregation is strongly linked to the pathogenesis of several incurable celland neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and type II diabetes (T2D). In vitro protein aggregation leads to a loss of function and complicates therapeutic application of a number of bioactive proteins or polypeptides such as insulin. Designing ...
04-Aug-2008
Nature Chemical Biology, online article

Biomimetic synthesis is an attempt to assemble natural products along biosynthetic lines without recourse to the full enzymatic machinery of nature. We exemplify this with a total synthesis of exiguamine A and the newly isolated natural product exiguamine B. The most noteworthy feature of this work is an oxidative endgame drawing from the complex chemistry of ...
01-Aug-2008
Biophysical Journal, online article
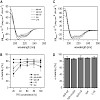
SNARE proteins mediate fusion of intracellular eukaryotic membranes and their -helical transmembrane domains are known to contribute to lipid bilayer mixing. Synthetic transmembrane domain peptides were previously shown to mimic the function of SNARE proteins in that they trigger liposome fusion in a sequence-specific fashion. Here, we performed a detailed ...
30-Jul-2008
The spore photoproduct is a unique photolesion, formed in spores upon irradiation with UV light; to investigate the properties of spore photoproduct containing DNA we have synthesized 5S and 5R lesion analogs and incorporated them into DNA.
Fpg (MutM) recognizes bulky N7-substituted-FapydG lesion using a novel and unproductive binding mode
21-Jul-2008
Chemistry & Biology, online article
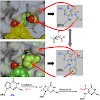
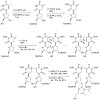
Fpg (MutM) is a bacterial base excision repair enzyme that removes the mutagenic and/or replication-block lesions 8-oxoguanine (8-oxodG) and imidazole-ring opened purines (Fapy-derivatives) from DNA. This work shows that Fpg and its eukaryote homologue Ogg1 recognize with high affinity FapydG and bulky N7-benzyl-FapydG (Bz-FapydG). The comparative crystal ...
28-May-2008
Imidazolone (dIz) is an abundant, highly mutagenic, and rather unstable DNA lesion that can cause dG!dC transversion mutations. dIz is generated in DNA by a variety of oxidative processes such as type I photooxidation. Herein we report the synthesis of a carbocyclic nucleoside analogue of dIz and of DNA containing this stabilized lesion analogue. The carbocyclic ...
22-May-2008
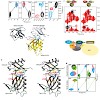
Targeted protein degradation is largely performed by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway, in which substrate proteins are marked by covalently attached ubiquitin chains that mediate recognition by the proteasome. It is currently unclear how the proteasome recognizes its substrates, as the only established ubiquitin receptor intrinsic to the proteasome is Rpn10/S5a ...
22-May-2008
The Journal Of Biological Chemistry, online article
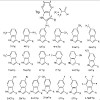
Non-canonical amino acids (NAA), as building blocks for peptides and proteins during ribosomal translation, represent a nearly infinite supply of novel functions. The specific selection, activation and tRNA-charging of amino acids by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (AARS) in the aminoacylation reaction are essential steps. In most cases, aminoacylation of NAA is a ...
19-May-2008
Analytical Biochemistry, online article

The serine/threonine kinase polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is critically involved in multiple mitotic processes and has been established as an adverse prognostic marker for tumor patients. Plk1 localizes to its substrates and its intracellular anchoring sites via its polo-box domain (PBD), which is unique to the family of polo-like kinases. Therefore, inhibition of ...
16-May-2008
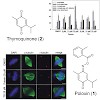
The serine/threonine kinase Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) is overexpressed in many types of human cancers, and has been implicated as an adverse prognostic marker for cancer patients. Plk1 localizes to its intracellular anchoring sites via its polo-box domain (PBD). Here we show that Plk1 can be inhibited by small molecules which interfere with its intracellular ...
22-Apr-2008
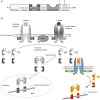
Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) are a family of transcription factors that are of central importance for cellular signaling and have therefore emerged as attractive target proteins for cell-permeable small molecules. This review outlines the basic concept of STAT signaling, the relevance of individual members of the STAT family for ...
15-Apr-2008
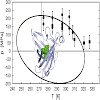
We have measured the equilibrium constant for the denaturation transition of the engineered fluorescein-binding lipocalin FluA as a function of pressure and temperature, taking advantage of the fact that the ligand’s fluorescence is almost fully quenched when complexed with the folded protein, but reversibly reappears on denaturation. From the equilibrium ...
10-Apr-2008
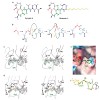
Pathogenic bacteria often use effector molecules to increase virulence.vIn most cases, the mode of action of effectors remains unknown. Strains of Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae (Pss) secrete syringolin A (SylA), a product of a mixed non-ribosomal peptide/polyketide synthetase, in planta1. Here we identify SylA as a virulence factor because a SylA-negative ...
09-Apr-2008
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article
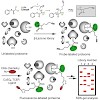
Evolution of multiresistant bacterial strains has meant that infectious diseases once again pose a major threat to public health. Since many antibiotics still target only a limited set of cellular functions, it is a desirable goal to expand the number and breadth of therapeutic targets as well as to gain a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms ...
02-Apr-2008
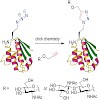
The importance of protein N terminus sequence composition for cell physiology was recognized more than two decades ago. However, its relevance for chemical protein engineering through an expanded genetic code was demonstrated only very recently. Nature changes the chemistry of the N terminus by posttranslational modifications (PTMs) such as longchain alkylation, ...
03-Mar-2008
Trauner Berkeley Webpage

2008 is great! We are very happy that Dirk Trauner will join CIPSM and the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry of the LMU in August 08 as a newly established CIPSM full professor. Dirk's research centers on the total synthesis of complex natural products and rationally designed molecular probes and their application to biological problems, especially in ...
27-Feb-2008
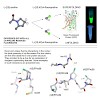
Proline residues affect protein folding and stability via cis/trans isomerization of peptide bonds and by the Cc-exo or -endo puckering of their pyrrolidine rings. Peptide bond conformation as well as puckering propensity can be manipulated by proper choice of ring substituents, e.g. Cc-fluorination. Synthetic chemistry has routinely exploited ringsubstituted ...
13-Feb-2008
www.bayerscheringpharma.de

Bayer Schering Pharma (BSP) and CIPSM sign a strategic partnership. The aim of both partners is to initiate a scientific exchange and to carry out joint projects in the field of protein chemistry. With this cooperation the partners wish to simplify and essentially accelerate the transfer of fundamental perceptions into applications, in order to score a leading ...
05-Feb-2008
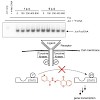
Molecular signals originating at the cell surface are conveyed by a complex system of interconnected signaling pathways to the nucleus. They converge at transcription factors, which in turn regulate the transcription of sets of genes which ultimately determine the cellular phenotype. Whereas enzymes involved in signaling pathways, that is, intracellular kinases ...
18-Jan-2008
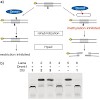
DNA methyltransferases convert deoxycytidine (dC) nucleobases in DNA into 5-methyldeoxycytidines (dCMe) using the cofactor S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the methyl group donor.Methylation of the canonical dC base, particularly in gene promoter regions, induces complex processes, which finally lead to the silencing of the corresponding gene. This epigenetic gene ...
18-Jan-2008
Analytical Biochemistry, online article
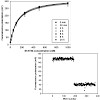
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b) is constitutively activated in many human tumors. Activity of STAT5b requires binding of its Src homology 2 (SH2) domain to certain phosphotyrosine-containing sequences. We have developed a highthroughput assay based on fluorescence polarization that allows screening of chemical libraries for compounds ...
18-Jan-2008
Analytical Biochemistry, online article
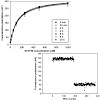
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (STAT5b) is constitutively activated in many human tumors. Activity of STAT5b requires binding of its Src homology 2 (SH2) domain to certain phosphotyrosine-containing sequences. We have developed a highthroughput assay based on fluorescence polarization that allows screening of chemical libraries for compounds ...
14-Jan-2008
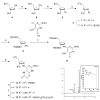
The oxidative DNA lesion, FaPydG rapidly anomerizes to form a mixture of the a and b anomer. To investigate the mutagenic potential of both forms, we prepared stabilized bioisosteric analogues of both configurational isomers and incorporated them into oligonucleotides. These were subsequently used for thermodynamic melting-point studies and for primerextension ...
03-Dec-2007
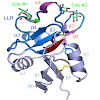
Langerin is a type II transmembrane oligosaccharide receptor on Langerhans cells (LCs), a prominent subclass of dendritic cells (DCs) that mediate immune responses in epithelia and play a role in HIV degradation. Its extracellular moiety comprises a neck region with several heptad repeats and an exposed carboxy-terminal calcium-type carbohydrate-recognition ...










