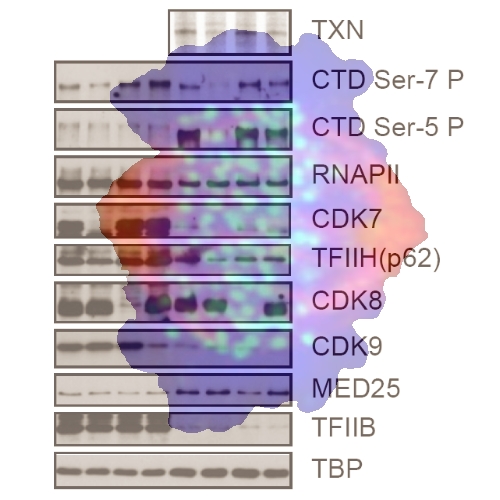
RNAPII CTD SER-7 phosphorylation is established in a mediator-dependent fashion
09-Nov-2009
JBC, 2009, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.046565 published on 09.11.2009
JBC, online article
The largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) carboxy-terminal heptarepeat domain (CTD) is subject to phosphorylation during initiation and elongation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Here we study the molecular mechanisms leading to phosphorylation of serine-7 (ser-7) in the human enzyme. Ser-7 becomes phosphorylated before initiation of transcription at promoter regions. We identify CDK7 as one responsible kinase. Phosphorylation of both ser-5 and ser-7 is fully dependent on the cofactor complex Mediator. A subform of Mediator associated with an active RNAPII is critical for preinitiation complex formation and CTD phosphorylation. The Mediator-RNAPII complex independently recruits TFIIB and CDK7 to core promoter regions. CDK7 phosphorylates ser-7 selectively in the context of an intact preinitiation complex. CDK7 is not the only kinase that can modify ser-7 of the CTD. ChIP experiments with chemical inhibitors provide evidence that other yet to be identified kinases further phosphorylate ser-7 in coding regions.