Research Area D - Publications 2021
03-Jun-2021
Nat Rev Cancer (2021), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-021-00363-z
Nat Rev Cancer, online article
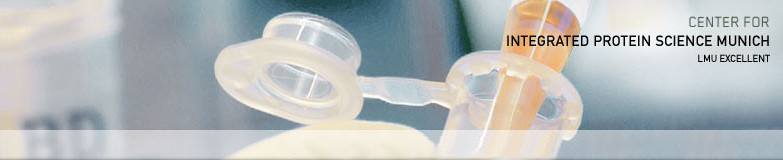
Interleukins and associated cytokines serve as the means of communication for innate and adaptive immune cells as well as non-immune cells and tissues. Thus, interleukins have a critical role in cancer development, progression and control. Interleukins can nurture an environment enabling and favouring cancer growth while simultaneously being essential for a ...
03-Jun-2021
Nat Biomed Eng (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00737-6
Nat Biomed Eng., online article
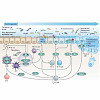
The efficacy of adoptive cell therapy for solid tumours is hampered by the poor accumulation of the transferred T cells in tumour tissue. Here, we show that forced expression of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 6 (whose ligand is highly expressed by human and murine pancreatic cancer cells and tumour-infiltrating immune cells) in antigen-specific T cells enhanced ...
21-Apr-2021
EMBO J (2021), e102277, https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2019102277
EMBO J, online article
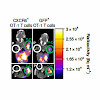
The ongoing outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) demonstrates the continuous threat of emerging coronaviruses (CoVs) to public health. SARS‐CoV‐2 and SARS‐CoV share an otherwise non‐conserved part of non‐structural protein 3 (Nsp3), therefore named as “SARS‐unique domain” (SUD). We previously found a yeast‐2‐hybrid ...
12-Mar-2021
Sci Rep 11, 5838 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84708-6
Scientific Reports, online article

Chemotherapy resistance is the main impediment in the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML). Despite rapid advances, the various mechanisms inducing resistance development remain to be defined in detail. Here we report that loss-of-function mutations (LOF) in the histone methyltransferase EZH2 have the potential to confer resistance against the ...
11-Mar-2021
J. Cell Biol. 2021 Vol. 220 No. 5 e202008030, https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202008030
J. Cell Biol., online article
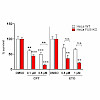
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are emerging as important effectors of the cellular DNA damage response (DDR). The RBP FUS is implicated in RNA metabolism and DNA repair, and it undergoes reversible liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) in vitro. Here, we demonstrate that FUS-dependent LLPS is necessary for the initiation of the DDR. Using laser microirradiation in ...