Concerted Activities of Distinct H4K20 Methyltransferases at DNA Double-Strand Breaks Regulate 53BP1 Nucleation and NHEJ-Directed Repair
24-Jul-2014
Cell Reports, 2014, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.013, Volume 8, Issue 2, p430–438 published on 24.07.2014
Cell Reports, online article
Cell Reports, online article
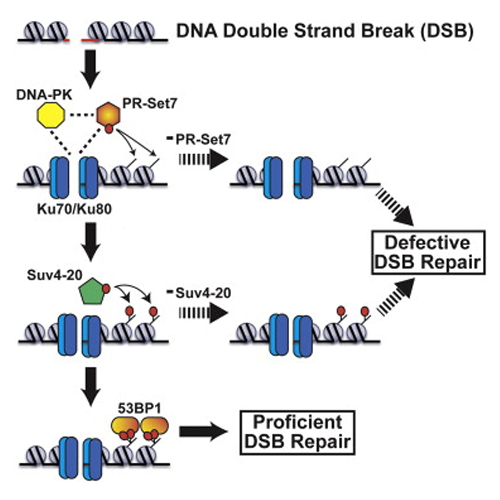
Although selective binding of 53BP1 to dimethylated histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20me2) at DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) is a necessary and pivotal determinant of nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)-directed repair, the enzymes that generate H4K20me2 at DSBs were unclear. Here, we determined that the PR-Set7 monomethyltransferase (H4K20me1) regulates de novo H4K20 methylation at DSBs. Rapid recruitment of PR-Set7 to DSBs was dependent on the NHEJ Ku70 protein and necessary for NHEJ-directed repair. PR-Set7 monomethyltransferase activity was required, but insufficient, for H4K20me2 and 53BP1 nucleation at DSBs. We determined that PR-Set7-mediated H4K20me1 facilitates Suv4-20 methyltransferase recruitment and catalysis to generate H4K20me2 necessary for 53BP1 binding. The orchestrated and concerted activities of PR-Set7 and Suv4-20 were required for proficient 53BP1 nucleation and DSB repair. This report identifies PR-Set7 as an essential component of NHEJ and implicates PR-Set7 as a central determinant of NHEJ-directed repair early in mammalian DSB repair pathway choice.